In the early days of electric cars, there were widespread worries about battery life and capacity degradation. However, real-world experience has proven these concerns largely unfounded. Electric vehicle (EV) batteries have shown remarkable longevity, often outlasting the lifespan of the vehicle itself. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the workings of EV batteries, addressing common misconceptions and shedding light on their impressive performance.
The Functioning of an EV Battery
Typically positioned beneath the car’s floor, an EV battery may appear as a large black slab. However, it is a sophisticated system designed to store and deliver electricity safely and efficiently over an extended period. Contrary to popular belief, the battery is not a single unit but comprises multiple individual modules interconnected by cables. These modules connect the battery pack to various components in the car, including the electric motor, brakes, charger, and control systems.
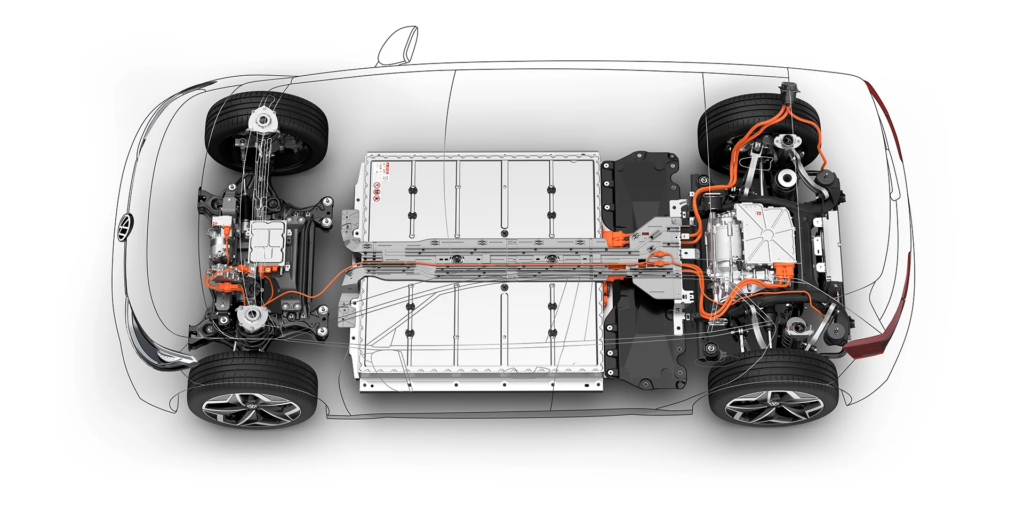
EV batteries primarily utilize Lithium-ion (Li-ion) or lithium polymer cells, similar to those found in mobile phones. Nonetheless, it is crucial to note that the operation of a car battery differs significantly from that of a phone battery. While phone batteries tend to lose performance relatively quickly, EV batteries consist of thousands of Li-ion cells that work together. When charging, chemical changes occur within the batteries to store electricity, which is subsequently released to power the motor when the vehicle is in motion. The capacity, size, volume, and weight of the battery pack directly influence the car’s range and cost.
Longevity of Electric Car Batteries
Modern EV batteries are engineered to endure the lifespan of the vehicle, meaning they remain in use unless they are damaged or scrapped. Initially, to reassure customers, some manufacturers implemented separate finance or leasing agreements for the car and battery. However, this approach unintentionally amplified concerns, creating confusion and fostering the false belief that EV batteries had a short lifespan and were expensive to replace.
Fortunately, as real-world experience has accumulated, it has become evident that EV batteries often outlast the car itself. To instill confidence, manufacturers now offer extended warranties specifically for the battery, surpassing the coverage for the rest of the vehicle. A typical warranty lasts around eight years or 100,000 miles, although many EV batteries exceed these estimates. For example, Tesla batteries are reported to have a lifespan of 300,000 to 500,000 miles.
Potential Issues and Charging Considerations
In most cases, problems arising from electric car batteries are related to the components connected to the battery rather than the battery itself. However, it is important to note that over time, the battery’s charge-holding capacity may decrease, albeit to a much lesser extent than with a phone battery. EV batteries have a fixed number of charge and discharge cycles, and their effectiveness gradually diminishes over time.
To mitigate these issues, EV batteries employ various protective mechanisms. For instance, the batteries are buffered, meaning that drivers cannot utilize the full power stored in them. This limitation reduces the number of cycles individual battery cells go through, prolonging their lifespan. Additionally, EV batteries feature cooling systems to maintain optimal temperature conditions, as lithium-ion batteries perform best between 15°C and 35°C. Sophisticated cooling systems prevent overheating, and in extreme cold conditions, batteries can be pre-heated to enhance performance.
Adopting good charging habits further safeguards the battery’s health and longevity. Charging an EV battery from 20% to 80% is considered optimal, as it reduces strain on the battery and extends its lifespan. Many EVs are equipped with features that regulate charging speed based on the battery level, allowing for faster charging within the 20% to 80% range. Additionally, smartphone apps can be used to schedule charging times and pre-heat the battery and cabin, optimizing energy efficiency.
Repair and Replacement Considerations
While rare, damage to EV batteries can occur in accidents. However, these incidents are generally infrequent, and EV batteries are well-protected within the vehicle’s structure. In the event of minor damage to the battery casing or cells, partial repairs are often possible. For example, Volkswagen’s MEB battery, used in their ID models, consists of several modules that can be individually replaced, minimizing costs compared to replacing the entire battery. Repair services and support centers are available to address battery-related issues and ensure proper diagnostics and repairs.
The Cost of Battery Replacement
The cost of replacing an EV battery varies depending on several factors. However, it is worth noting that the battery’s lifespan often exceeds the duration of the original vehicle, and recycling is a common practice. Comparable to conventional vehicles, where failures of specific control units typically prompt scrapping, EV batteries tend to outlast the car’s functional life.
According to BloombergNEF’s 2021 annual battery price survey, battery prices are projected to reach around $100 per kilowatt-hour. For instance, replacing a 100 kWh battery, such as the one in a Tesla Model S, would cost approximately $10,000 (£9,000 at the exchange rate of October 2022).
Overall, EV batteries have demonstrated their reliability, surpassing initial concerns regarding longevity and performance. With proper care, adherence to good charging habits, and periodic maintenance, electric car owners can enjoy the full benefits of their vehicles for an extended period.


